In this lab, we will be using 2N 3904 transistor.
Step 1) Testing the Transistor
When current is allowed to go into the base pin of the transistor, the LED turns on as the transistor opens up, and allows a higher output current from the emitter pin. This means......the transistor is FUNCTIONAL!
Step 2) Examining the sensitivity of the transistor
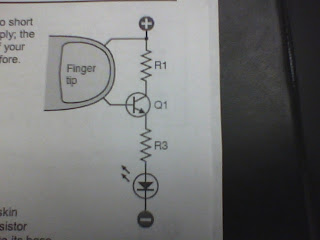
We will limit the control current to very small by using the hugh resistance in human's skin.
Human's skin resistance has an average resistance of 400 kilo ohm.
No current is going through the LED if the controlling circuit is opened.
When the controlling circuit is closed, the LED is lit with a very dim light. The transistor is opened even with a very small current.
Transistor are extemely sensitive!!
For the last Experiment, we tests the beta value of our transister as well as it saturation limit:
We first connect a ammeter to the in series to the base, and another ammerter in series with the emitter.
Transistorsare used to limit the current to protect the transistor from over heating or burning any of the circuit's components.
Here are the results:
From the graph,
the slope gives our beta value of approximately 80;
the transistor begins to saturate when the base current reaches 0.75mA as the slope of the graph
begins to reaches 0.









No comments:
Post a Comment